Prompt Evaluation
Notes on prompt evaluation from Anthropic's course on Claude.
Prompt Engineering and Evaluation
Prompt Evaluation
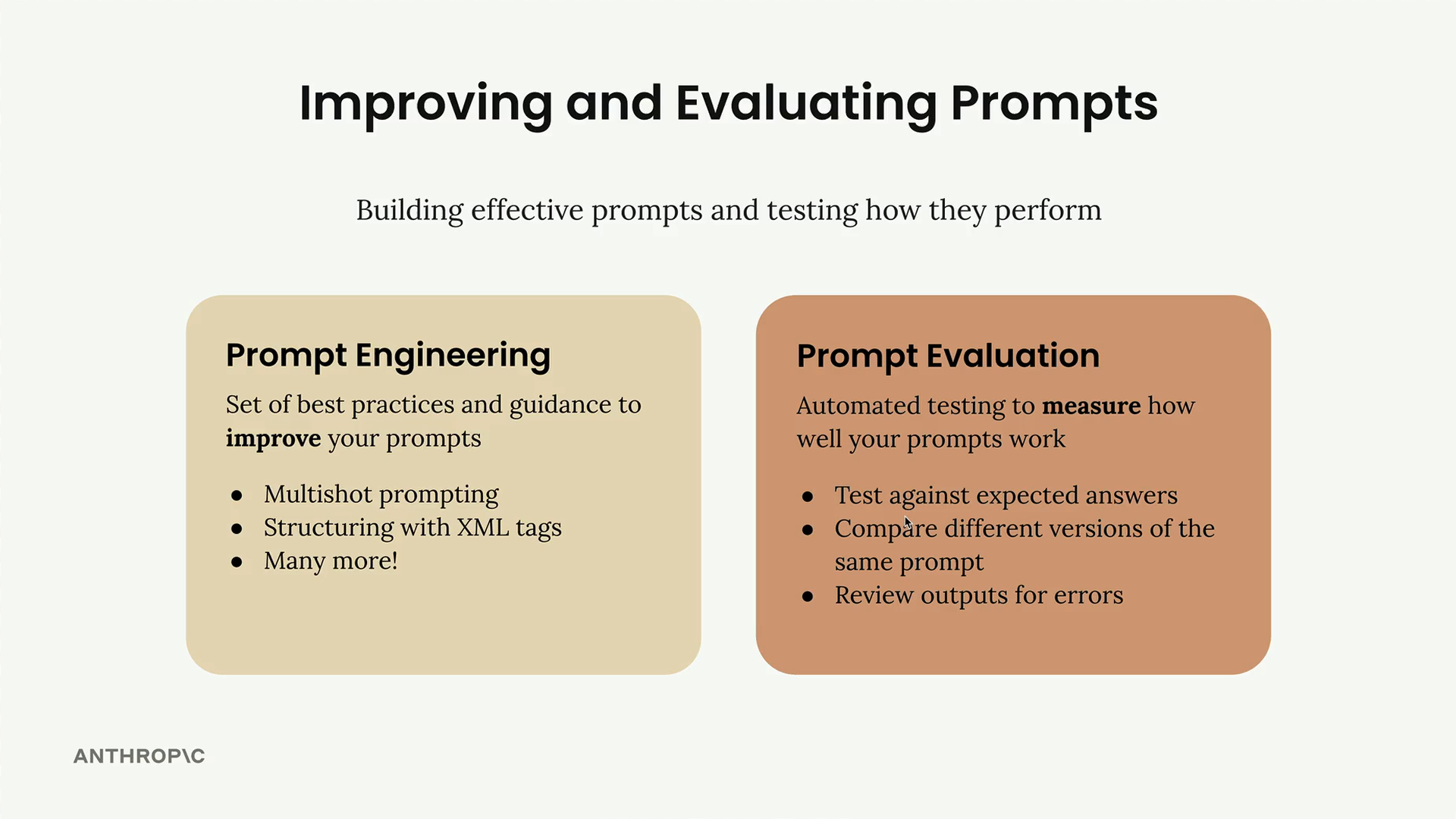
Measuring the effectiveness of prompts through automated testing:
- Test against expected answers
- Compare model versions against the same prompt
- Review the output for errors, mistakes, policy
Evaluation Pipelines
Generate objective metrics about performance:
- Identify weaknesses pre-prod
- A-B test prompts
- Iterate based on measurement
- Increase reliability of your AI app
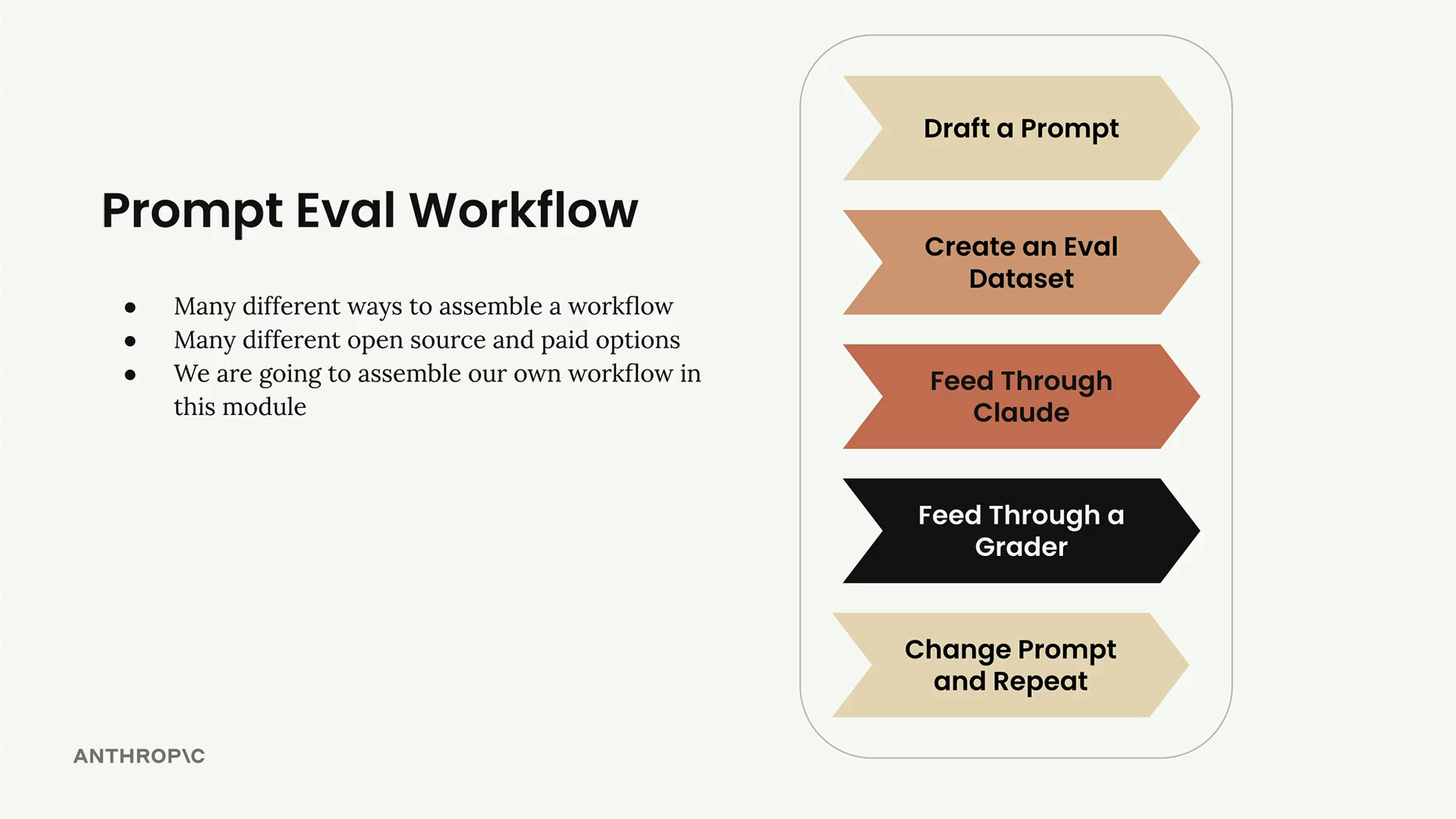
Eval data set - set of inputs for evaluation purposes, can be done with smaller faster LLMs
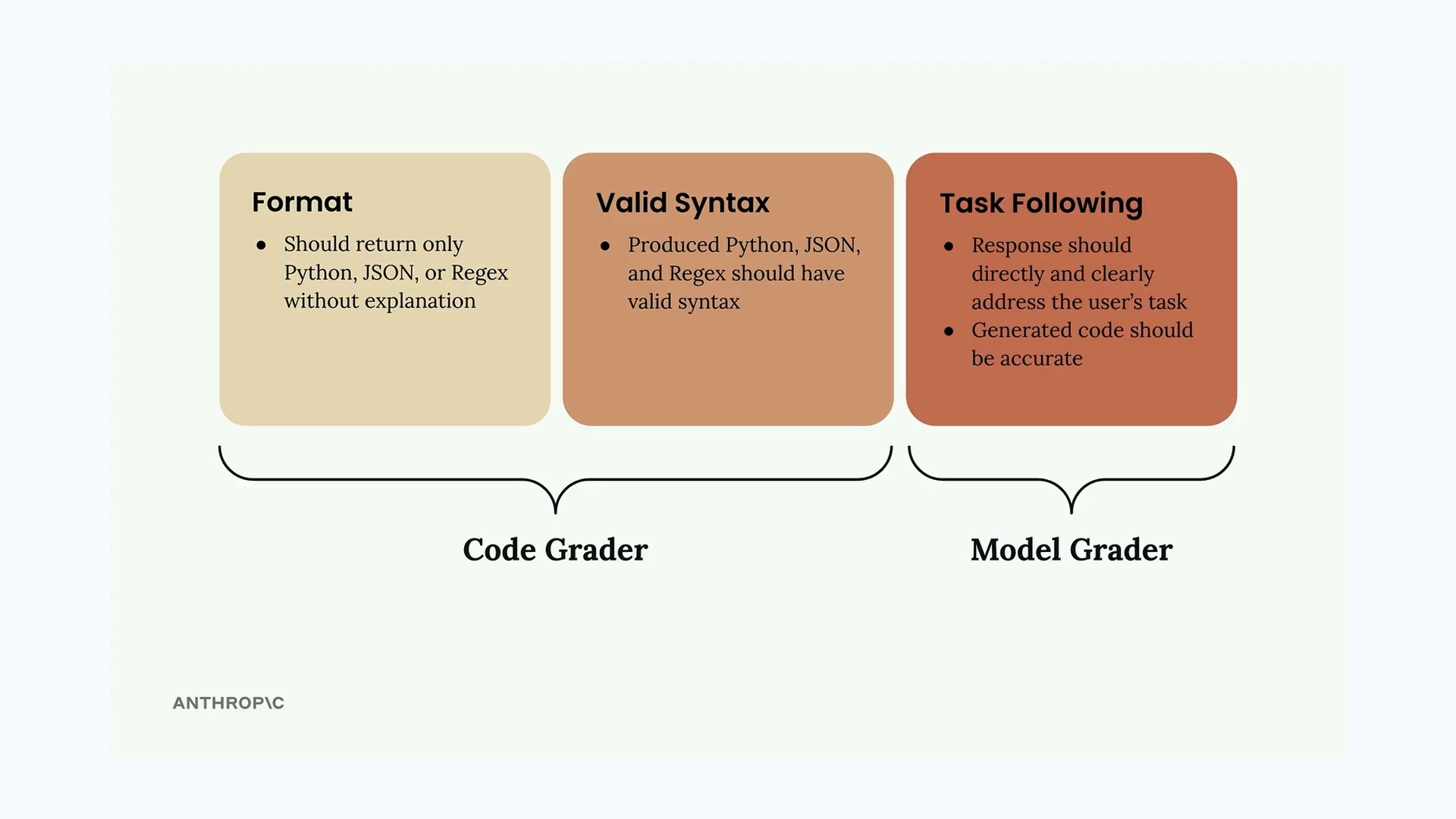
Grader - grade the quality of the response of the LLM. Numerical grading allows for a more objective measurement of prompt performance.

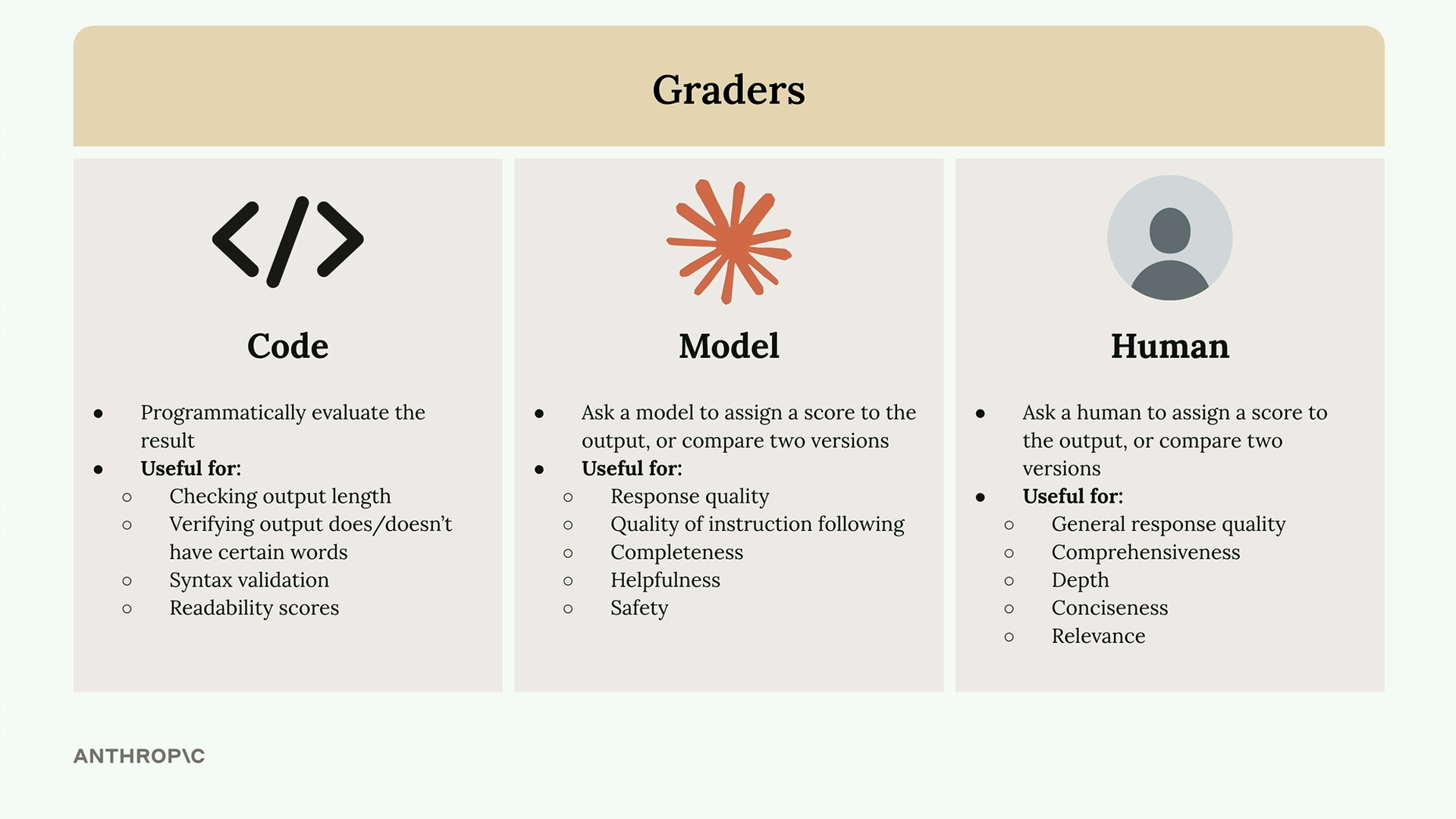
Graders
Take the model output which has been generated from the evaluation data.
The grader provides measureable feedback on the model output.
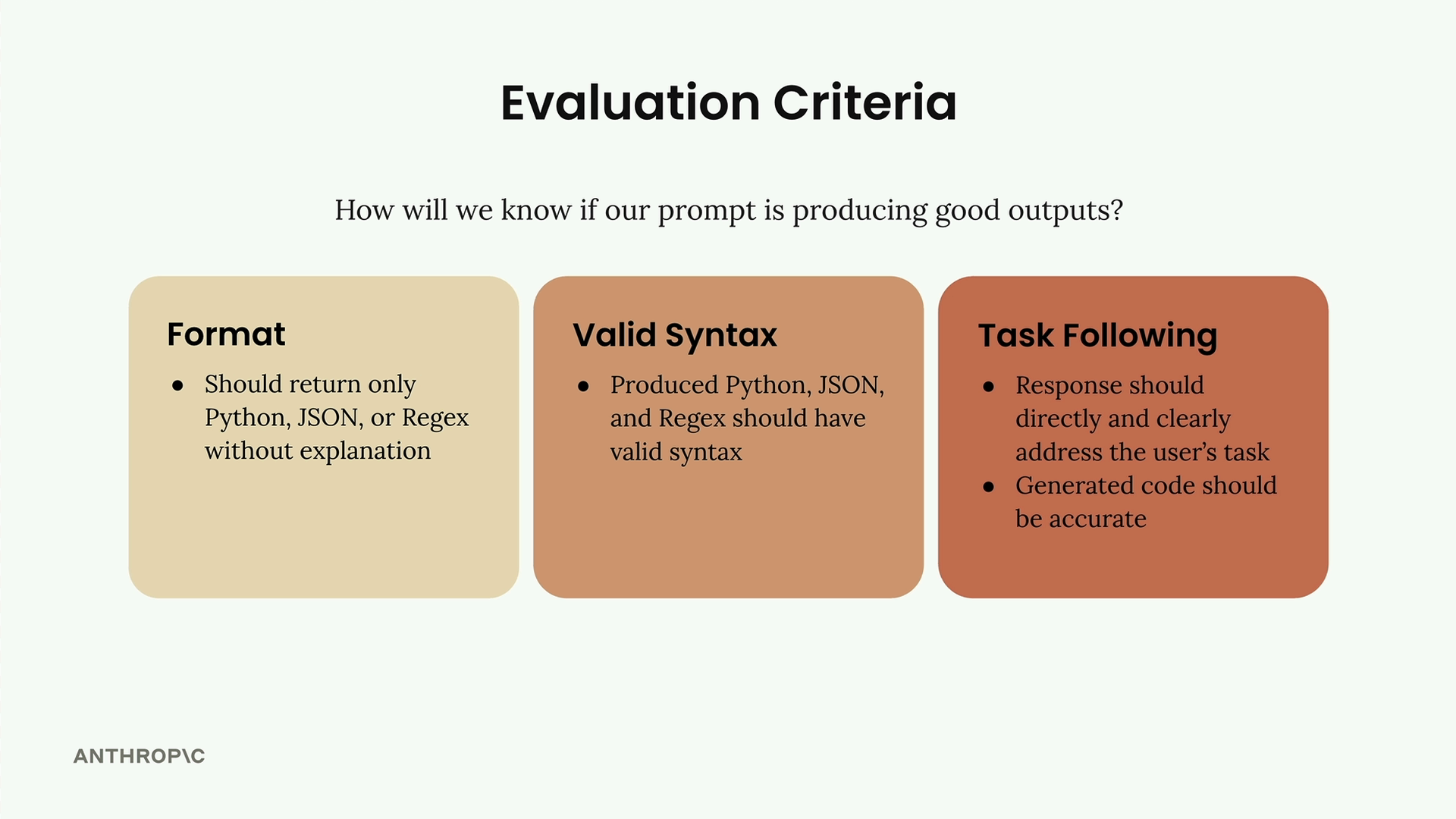
Evaluation Criteria
Prompt Engineering
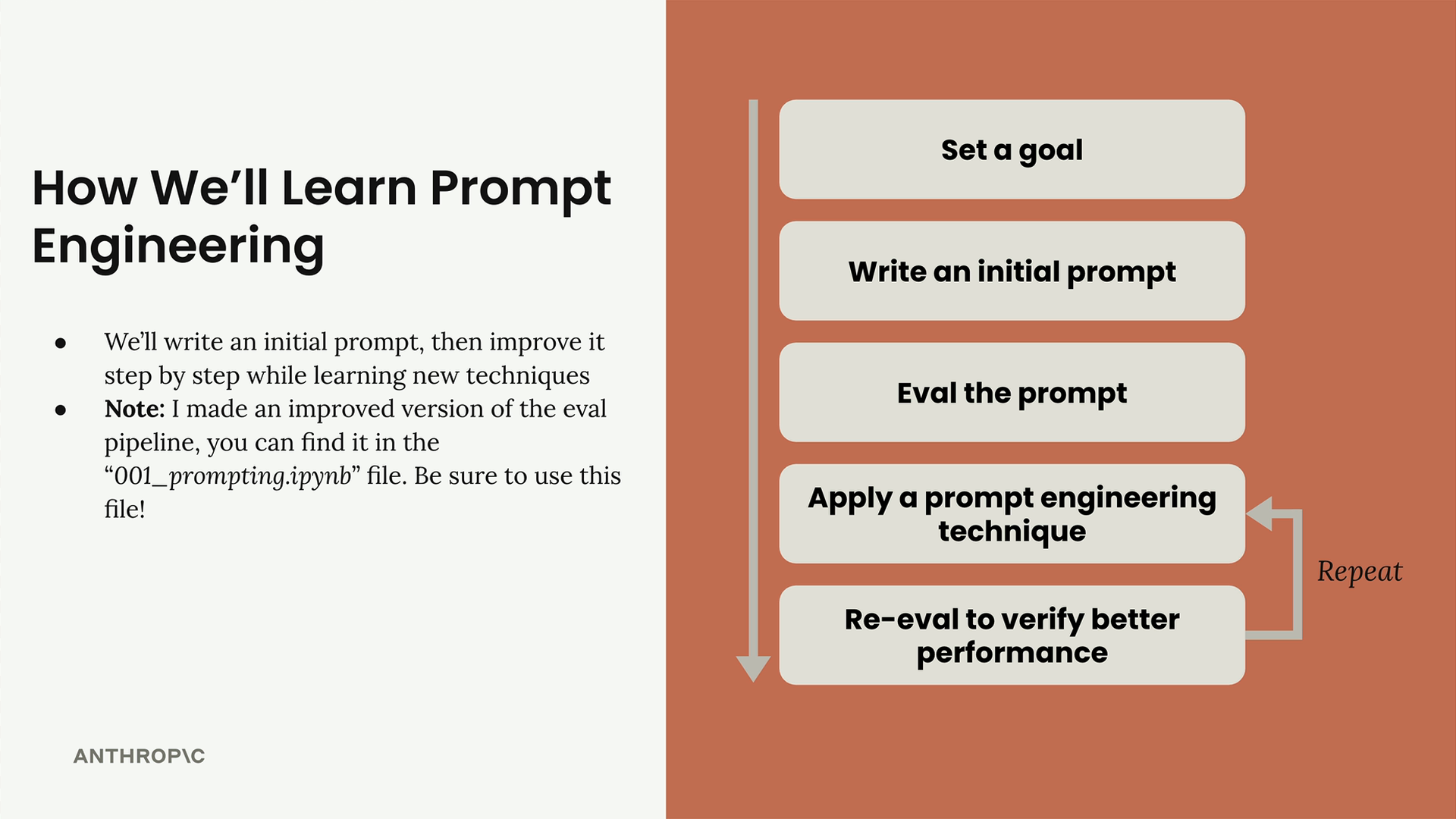
Developing high quality prompts is an iterative process:
Being Clear and Direct

The key takeaway is that Claude responds best when you treat it like a capable assistant who needs clear direction rather than someone who has to guess what you want. Start strong with a direct action verb, be specific about the task, and you'll see better results right away.
- Be specific about what you want
- Provide guidelines or steps as part of the prompt
When providing guidelines we can provide qualities like word count, or we can provide steps:

Output guidelines should be used in every prompt to ensure consistent and useful results.
Process steps should be for more complex problems e.g. troubleshooting, decision making, critical thinking, considering multiple angles.
Structure with XML Tags
Seperate distinct portions of a prompt using XML tags:

Useful to add XML tags when:
- Including large amounts of context or data
- Mixing different types of content (code, documentation, data)
- You want to be extra clear about content boundaries
- Working with complex prompts that interpolate multiple variables
Using Examples
Provide examples for input and output as part of the prompt and to handle corner cases:
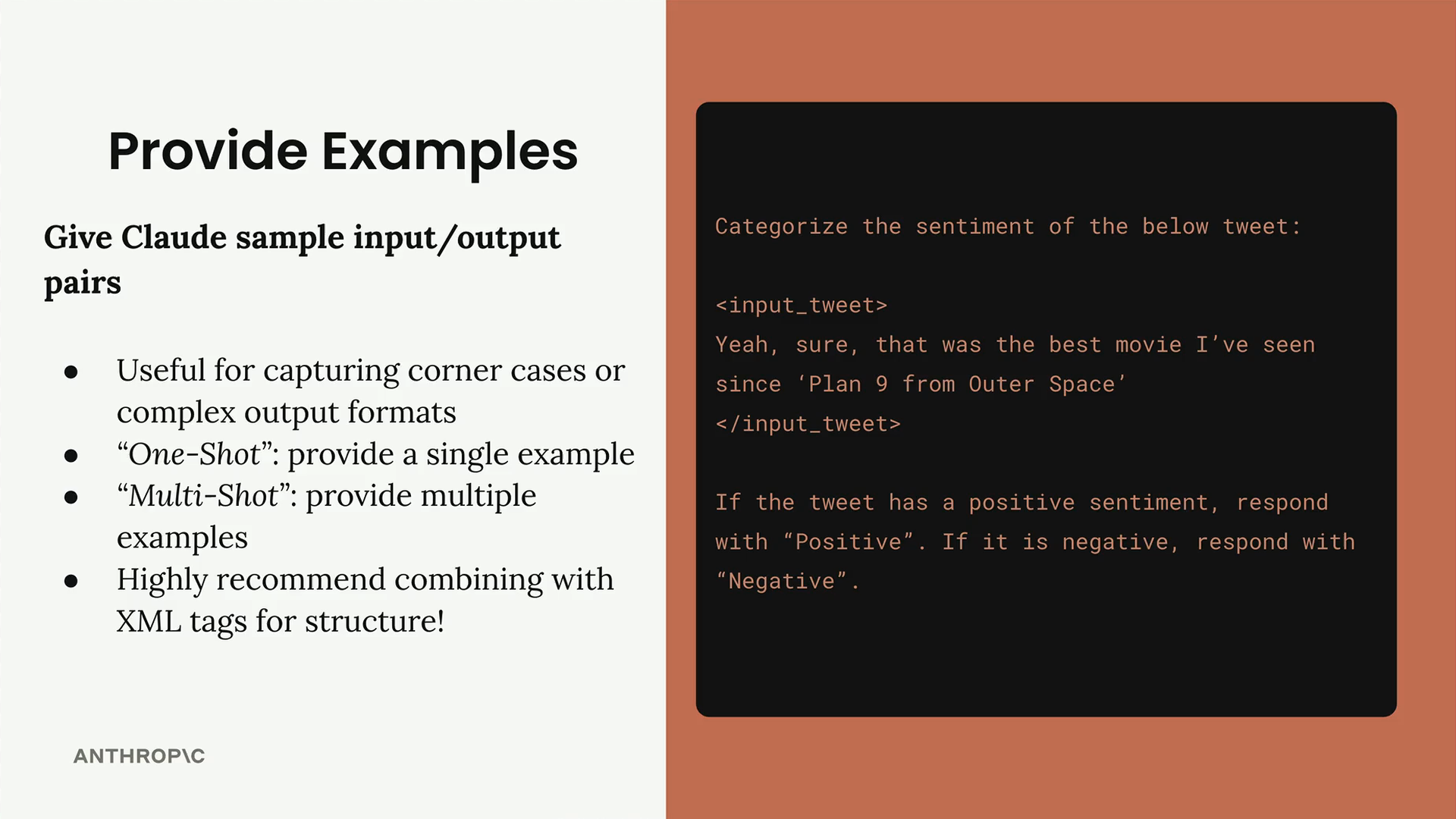
- Capturing corner cases or edge scenarios
- Defining complex output formats (like specific JSON structures)
- Showing the exact style or tone you want
- Demonstrating how to handle ambiguous inputs
You can also explain why the output is good to add more context for the model.
