Backend for Frontend
An architectural design pattern for supporting multiple frontends, the Backend for Frontend pattern is also intrinsicly linked to security.

What is the BFF Pattern?
Let's say we have to support multiple client types - these could be different frontends like web and mobile.
We can create a distinct backend service to handle requests and streams from each specific type of client - each of these backends talks to our core services in a proxy like fashion whilst handling all integration+translation for the client type they service.
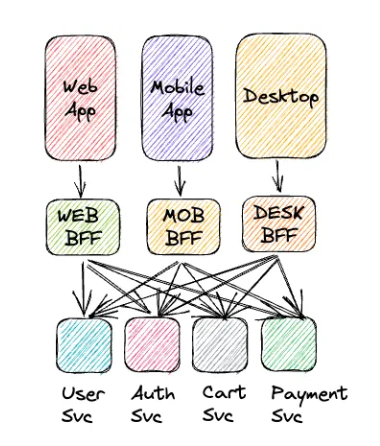
Source: Elif Cetiner, Medium
This gives us the benefits of a tailored solution for our client types and we can make more specific design choices and even optimise along the most relevant dimension for specific client types e.g. data transfer costs.
This does result in more backend services to maintain (did someone say service mesh?), but we get the benefits of reduced coupling between our core backend services and the client types we want to provide services too.
What's Security Got To Do With It?
Sometimes the functionality we take for granted in products that is fundamentally about user convenience comes at great cost, complications and changing best practice. A good example of this is not having to log back into websites every 5 minutes.
The OWASP guidance for handling cryptographic secrets in an insecure/untrusted environment is currently....don't do it.
Session Tokens vs JWT
JWTs can be difficult to revoke and there are whole classes of attacks (XSS to steal and CSRF to use) to either steal JWTs or get access to the permissions they may provide.
It's also often tempting to use JWT packing and encode way too much information in them because, well, it's the easy and convenient thing to do.
Session tokens use the cookie header and should be http-only (not accessible by JS in the browser) and secure (https only). The session token is used to identify a session which is "stored" server side only. This makes it easier to revoke, rotate and also to handle things like session invalidation on logout.

Your Backend for Frontend stores the session and authenticates with your internal core backend services using JWTs or OAUTH in a traditional microservices approach.
This means that things like refresh tokens are held in your servers on the backend and not on the insecure/untrusted client which is only given the http-only cookie.
Recommended BFF Security Flow
-
Login via OAuth2 Authorization Code Flow + PKCE (code verifier and code challenge)
-
Store tokens server side
-
Issue secure HttpOnly cookie to clients
-
Frontend communicates via the BFF only
-
BFF adds access tokens when calling internal APIs
-
SameSite cookies + CSRF token for POST/PUT/DELETE
-
Session invalidation on logout
Links and Resources
https://cheatsheetseries.owasp.org/cheatsheets/Session_Management_Cheat_Sheet.html - OWASP Session Management Cheat Sheet
https://auth0.com/blog/refresh-tokens-what-are-they-and-when-to-use-them/
